ERP Program – In the realm of modern business management, efficiency, organization, and integration are key factors for success. To meet these demands, many companies turn to Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) programs.
These sophisticated software solutions have become essential tools for managing a wide range of business activities, from finance and human resources to supply chain management and customer relations.
In this article, we’ll explore the significance of ERP programs, their core features, benefits, and considerations for implementation.

Understanding ERP Programs
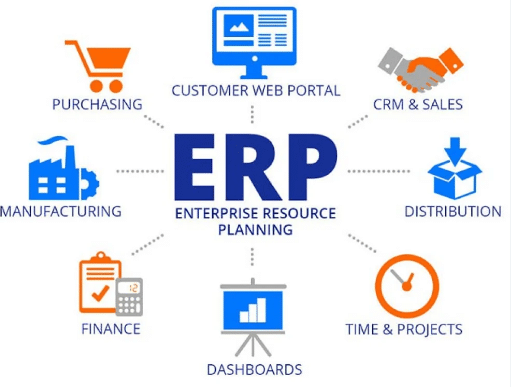
ERP programs are comprehensive software suites designed to integrate and streamline various business processes across an organization. They serve as centralized hubs that consolidate data and facilitate communication between different departments, enabling seamless coordination and collaboration. ERP programs typically include modules for finance, human resources, inventory management, procurement, manufacturing, sales, and customer relationship management (CRM).
Key Features of ERP Programs
- Finance Management: ERP programs offer robust financial management capabilities, including general ledger, accounts payable, accounts receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting. These features provide real-time visibility into financial transactions, facilitate accurate record-keeping, and support compliance with accounting standards and regulations.
- Human Resources Management: ERP programs encompass modules for managing various HR functions, such as payroll processing, employee records management, benefits administration, performance evaluation, and workforce planning. These features streamline HR processes, improve employee productivity, and ensure regulatory compliance.
- Supply Chain Management: ERP programs include tools for optimizing supply chain operations, including inventory management, procurement, order processing, logistics, and demand forecasting. By providing end-to-end visibility into the supply chain, these features enable organizations to reduce costs, minimize lead times, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Manufacturing Management: For manufacturing companies, ERP programs offer modules for production planning, scheduling, shop floor control, quality management, and product lifecycle management. These features support efficient manufacturing processes, ensure product quality, and enable agile response to changing market demands.
- Sales and CRM: ERP programs include CRM modules that enable organizations to manage customer interactions, track sales leads, analyze customer data, and streamline marketing campaigns. These features help organizations build strong customer relationships, increase sales effectiveness, and drive revenue growth.
Benefits of ERP Programs
- Streamlined Operations: By integrating core business functions into a single platform, ERP programs eliminate data silos and streamline workflows, reducing manual effort and operational inefficiencies.
- Improved Decision-Making: ERP programs provide real-time data insights and analytics, empowering decision-makers with actionable information for strategic planning and performance optimization.
- Enhanced Collaboration: With centralized data and standardized processes, ERP programs foster collaboration and communication across departments, promoting cross-functional teamwork and alignment towards common goals.
- Scalability: ERP programs are scalable solutions that can adapt to the evolving needs of businesses, supporting growth and expansion without requiring significant changes to the system architecture.
- Compliance and Risk Management: ERP programs help organizations maintain compliance with regulatory requirements and mitigate risks by enforcing standardized processes, ensuring data integrity, and providing audit trails for transactions.
Considerations for ERP Program Implementation
While the benefits of ERP programs are significant, successful implementation requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing management. Some key considerations include:
- Needs Assessment: Conduct a thorough analysis of business requirements and objectives to identify the most suitable ERP solution and modules for your organization.
- Vendor Selection: Evaluate ERP vendors based on factors such as industry expertise, product functionality, scalability, support services, and total cost of ownership.
- Customization vs. Configuration: Determine whether customization or configuration is necessary to align the ERP program with your organization’s unique processes and requirements.
- Data Migration: Plan and execute data migration activities carefully to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and integrity of data transferred to the new ERP system.
- Training and Change Management: Provide comprehensive training and support to end-users to facilitate adoption and minimize resistance to change during the implementation process.
- Performance Optimization: Monitor system performance closely and optimize configuration settings as needed to ensure optimal performance and scalability.
- Security and Compliance: Implement robust security measures and data protection protocols to safeguard sensitive information and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ERP programs play a vital role in streamlining business operations, improving efficiency, and driving growth in today’s competitive landscape. With their comprehensive features, real-time insights, and scalability, ERP programs empower organizations to adapt to changing market dynamics and achieve operational excellence. However, successful implementation requires careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and ongoing management. By considering key factors such as needs assessment, vendor selection, customization, data migration, training, and security, organizations can maximize the benefits of ERP programs and position themselves for long-term success in the digital age.
Maximizing the Potential of ERP Programs
To fully harness the potential of ERP programs, organizations must embrace a strategic approach to implementation and utilization. Here are some additional strategies for maximizing the benefits of ERP programs:
- Continuous Improvement: ERP programs should not be viewed as static solutions but rather as dynamic platforms that evolve with the needs of the organization. Continuous improvement processes, such as regular system audits, user feedback sessions, and performance reviews, enable organizations to identify areas for optimization and enhancement.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: To stay ahead of the curve, organizations should explore opportunities to integrate ERP programs with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies can enhance the capabilities of ERP programs by enabling predictive analytics, automation of routine tasks, and real-time monitoring of business processes.
- Mobile Accessibility and Remote Work: With the rise of remote work and mobile workforce trends, organizations should prioritize mobile accessibility features in their ERP programs. Mobile applications enable employees to access critical business data and perform tasks from anywhere, facilitating productivity and collaboration across distributed teams.
- Data-driven Decision Making: ERP programs generate vast amounts of data that can be leveraged to drive data-driven decision-making. Organizations should invest in analytics tools and data visualization capabilities to extract actionable insights from ERP data. By analyzing trends, identifying patterns, and predicting outcomes, organizations can make informed decisions that drive business growth and innovation.
- Strategic Partnerships: Establishing strategic partnerships with ERP vendors, consultants, and industry experts can provide valuable support and guidance throughout the ERP journey. Vendors can offer insights into best practices, provide training and certification programs, and offer ongoing support and maintenance services to ensure the success of ERP programs.
- User Adoption and Training: User adoption is critical to the success of ERP programs. Organizations should invest in comprehensive training programs to educate employees on how to effectively use the ERP system. Additionally, fostering a culture of innovation, collaboration, and continuous learning encourages employees to embrace ERP programs as valuable tools for achieving organizational goals.
- Regular Maintenance and Updates: ERP programs require regular maintenance and updates to address security vulnerabilities, performance issues, and compatibility issues with