
Blog
-

Oracle HR
Oracle HR-In today’s fast-paced business world, managing human resources efficiently is crucial for organizations of all sizes. From recruitment and onboarding to payroll and talent management, human resource management plays a pivotal role in an organization’s success. Oracle, a global leader in enterprise software and cloud solutions, offers a comprehensive Human Resources Management System (HRMS) known as Oracle HR. In this in-depth guide, we will explore Oracle HR’s features, benefits, and how it can streamline HR processes for businesses in various industries.
-

ERP for Small Business
ERP for Small Business-In the fast-paced and competitive landscape of small businesses, the integration of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions has become a game-changer. This article aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of ERP for small businesses, outlining its definition, evolution, key features, benefits, industry applications, implementation strategies, and future trends.

A. Definition and Overview
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) for small businesses is a set of integrated software applications designed to streamline and automate various business processes, enhancing efficiency, collaboration, and decision-making. This section introduces the concept of ERP for small businesses and outlines its core functionalities.
B. Evolution of ERP for Small Businesses
The evolution of ERP for small businesses is essential to understanding its current capabilities. This subsection traces the historical development of ERP solutions tailored for small enterprises, highlighting the technological advancements that have contributed to their accessibility and effectiveness.
II. Key Features of ERP for Small Businesses
ERP solutions for small businesses come with a set of key features that cater to the specific needs of smaller enterprises. This section breaks down these essential functionalities and explores how they contribute to the efficiency and growth of small businesses.
1. Scalability and Affordability
Scalability is crucial for small businesses experiencing growth. This subsection discusses how ERP solutions for small businesses offer scalability without compromising affordability, allowing organizations to expand without a significant financial burden.
2. Financial Management
Efficient financial management is a cornerstone of small business success. Explore how ERP solutions streamline accounting, invoicing, and financial reporting processes, providing real-time insights for informed decision-making.
3. Inventory and Supply Chain Management
For small businesses involved in product-based operations, effective inventory and supply chain management are paramount. This part delves into how ERP solutions optimize inventory control, order processing, and supply chain visibility.
4. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Building strong customer relationships is a key focus for small businesses. Learn how ERP solutions with integrated CRM functionalities help manage customer interactions, sales, and marketing efforts, fostering customer loyalty.
III. Benefits of ERP for Small Businesses
The adoption of ERP solutions brings forth a myriad of benefits for small businesses seeking operational efficiency and growth. This section systematically outlines these advantages, showcasing how ERP positively impacts various facets of small business management.
A. Streamlined Processes and Increased Efficiency
ERP solutions streamline business processes, reducing manual efforts and increasing overall operational efficiency. Explore how small businesses benefit from streamlined workflows and improved productivity.
B. Data Accuracy and Informed Decision-Making
Accurate data is essential for decision-making. This subsection discusses how ERP solutions for small businesses provide a single source of truth, ensuring data accuracy and empowering organizations to make informed decisions.
C. Cost Savings and Improved Financial Health
Cost savings are a compelling advantage of ERP adoption. Delve into how small businesses benefit from reduced operational costs, improved financial visibility, and enhanced overall financial health.
IV. Industry Applications of ERP for Small Businesses
The versatility of ERP solutions for small businesses extends across various industries. This section explores how these solutions are applied in sectors such as retail, services, manufacturing, and more, showcasing their adaptability to diverse business environments.
A. Retail Industry
Discover how small retailers leverage ERP solutions for inventory management, order processing, and customer relationship management, enhancing their competitiveness in the market.
B. Service-Based Businesses
For service-oriented small businesses, effective project management and resource allocation are critical. Explore how ERP solutions streamline service delivery, optimize project workflows, and improve overall efficiency.
C. Manufacturing Sector
In the manufacturing sector, ERP solutions play a vital role in production planning, inventory control, and supply chain management. This component discusses how small manufacturers benefit from ERP adoption.
V. Implementation Strategies for ERP in Small Businesses
Implementing ERP solutions in small businesses requires careful planning and execution. This section outlines key strategies for a successful ERP implementation, covering considerations such as data migration, user training, and customization.
A. Tailored Implementation Plans
Small businesses may have unique needs. Explore how creating tailored implementation plans ensures that ERP solutions align with the specific requirements and goals of each small business.
B. Data Migration and Integration
Data migration is a critical aspect of ERP implementation. This subsection discusses best practices for data migration and integration to ensure a seamless transition to the new ERP system.
C. User Training and Change Management
User adoption is pivotal for ERP success. This part emphasizes the importance of comprehensive user training programs and effective change management strategies to facilitate a smooth transition for employees.
VI. Challenges in ERP Implementation for Small Businesses
While the benefits of ERP adoption are substantial, challenges may arise during implementation. This section identifies common challenges faced by small businesses adopting ERP solutions and provides insights into overcoming these hurdles.
A. Limited Resources and Budget Constraints
Small businesses often face resource and budget constraints. Explore strategies to address these limitations and ensure a cost-effective and efficient ERP implementation.
B. Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a common challenge in any ERP implementation. This component delves into strategies for overcoming employee resistance and fostering a positive attitude towards the new ERP system.
C. Customization Complexity
Customization is essential for aligning ERP solutions with specific business needs. Delve into the challenges associated with customization complexity and find guidance on striking the right balance.
VII. Case Studies: Successful ERP Implementations in Small Businesses
Real-world examples provide tangible evidence of the effectiveness of ERP solutions in small businesses. This section presents case studies of small businesses that have successfully implemented ERP solutions, showcasing the transformative impact on their operations.
A. Local Retailer: Optimizing Inventory and Sales
Explore how a local retailer optimized inventory management, streamlined sales processes, and improved customer satisfaction through the successful implementation of ERP.
B. Boutique Consulting Firm: Enhancing Project Management
Delve into the case study of a boutique consulting firm that leveraged ERP to enhance project management, resource allocation, and overall service delivery efficiency.
VIII. Future Trends in ERP for Small Businesses
The landscape of ERP for small businesses is continually evolving. This section explores emerging trends and innovations that are expected to shape the future of ERP solutions for small enterprises.
A. Cloud-Based Solutions and Remote Accessibility
Explore the growing importance of cloud-based ERP solutions for small businesses and how remote accessibility is becoming a key trend in the evolving ERP landscape.
B. Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Examine the role of artificial intelligence in enhancing ERP functionalities for small businesses, including automation, predictive analytics, and intelligent decision support.
C. Mobile Applications for On-the-Go Management
Discover how the integration of mobile applications is becoming a trend, allowing small business owners and managers to access key ERP functionalities on-the-go.
IX. Selecting the Right ERP Solution for Small Businesses
Choosing the right ERP solution is a critical decision for small businesses. This section provides guidance on key considerations and factors to weigh when selecting the most suitable ERP solution for specific organizational needs.
A. Scalability and Flexibility
Evaluate the scalability and flexibility of ERP solutions to ensure they can grow with the business and adapt to changing needs without significant disruptions.
B. User-Friendly Interface and Accessibility
Consider the user-friendliness of ERP solutions and the accessibility of key features. This subsection discusses the importance of an intuitive interface for small business users.
C. Vendor Support and Training Programs
Assess the support and training programs offered by ERP vendors to ensure a smooth implementation process and ongoing assistance for small businesses.
X. Conclusion
In conclusion, ERP solutions for small businesses stand as catalysts for growth and efficiency, offering a comprehensive suite of tools to streamline operations and elevate business management. From their historical evolution to their current role in diverse industries, ERP solutions have consistently adapted to meet the unique needs of small businesses. As small enterprises continue to seek powerful, scalable, and cost-effective solutions, the future holds exciting possibilities with trends such as cloud-based solutions, AI integration, and mobile applications reshaping the ERP landscape.
-
ERP Online
ERP Online-In the ever-evolving landscape of business technologies, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) has undergone a significant transformation with the advent of ERP Online solutions. This article aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of ERP Online, focusing on its definition, evolution, key features, benefits, implementation strategies, and the future trends that are reshaping the way organizations manage their resources and operations.

A. Definition and Overview
ERP Online represents a paradigm shift in how businesses approach resource planning and management. This section defines ERP Online, highlighting its cloud-based nature and outlining the fundamental concepts that set it apart from traditional ERP systems.
B. Evolution of ERP Online
The evolution of ERP Online is essential to understanding its current capabilities. This subsection traces the historical development of ERP Online solutions, exploring the technological advancements that have paved the way for cloud-based ERP to become a cornerstone of modern business management.
II. Key Features of ERP Online
Understanding the key features of ERP Online is crucial for organizations considering a shift to cloud-based solutions. This section breaks down the core functionalities that define ERP Online and explores how these features contribute to enhanced agility and efficiency.
1. Cloud-Based Infrastructure
The cloud-based infrastructure is the foundation of ERP Online. This subsection delves into the benefits of cloud deployment, including accessibility, scalability, and reduced infrastructure costs.
2. Real-Time Data Access and Collaboration
One of the hallmarks of ERP Online is its ability to provide real-time data access and collaboration. Explore how this feature fosters better communication and decision-making across the organization.
3. Mobile Accessibility
With the rise of remote work, mobile accessibility has become a crucial feature. This component discusses how ERP Online solutions empower users to access critical information anytime, anywhere, using mobile devices.
4. Integration Capabilities
Integration with other business systems is a key strength of ERP Online. This part explores how seamless integration enhances data flow and eliminates silos, creating a holistic view of organizational processes.
III. Advantages of Adopting ERP Online
The adoption of ERP Online brings forth a plethora of advantages for organizations seeking to modernize their operations. This section systematically outlines these benefits, showcasing how ERP Online positively impacts various facets of organizational management.
A. Cost Savings and Resource Efficiency
Explore how ERP Online solutions contribute to cost savings by eliminating the need for extensive hardware infrastructure, reducing maintenance costs, and optimizing resource utilization.
B. Enhanced Security Measures
Security is a top concern in the digital age. This subsection discusses how ERP Online solutions implement robust security measures, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
C. Flexibility and Scalability
Flexibility and scalability are inherent to ERP Online. Discover how organizations can easily adapt to changing business needs and scale their ERP solutions as they grow.
IV. Implementation Strategies for ERP Online
Implementing ERP Online requires careful planning and execution. This section outlines key strategies for a successful ERP Online implementation, addressing considerations such as data migration, user training, and change management.
A. Data Migration Planning
Effective data migration is critical for a smooth transition to ERP Online. Explore strategies for planning and executing data migration, ensuring minimal disruption and data integrity.
B. User Training and Change Management
User adoption is pivotal for ERP success. This part emphasizes the importance of comprehensive user training programs and effective change management strategies to facilitate a smooth transition for employees.
C. Vendor Selection and Collaboration
Choosing the right ERP Online vendor is a crucial decision. This subsection provides guidance on selecting a reliable vendor, assessing their capabilities, and fostering a collaborative partnership.
V. Case Studies: Successful ERP Online Implementations
Real-world examples provide tangible evidence of the effectiveness of ERP Online solutions. This section presents case studies of organizations that have successfully implemented ERP Online, showcasing the transformative impact on their operations.
A. Global Retailer: Streamlining Supply Chain Operations
Explore how a global retailer streamlined its supply chain operations and improved inventory management through the successful implementation of ERP Online.
B. Tech Startup: Scaling Operations with Cloud ERP
Delve into the case study of a tech startup that leveraged ERP Online to scale its operations rapidly, enhance collaboration among remote teams, and achieve significant business growth.
VI. Challenges in ERP Online Implementation
While the benefits of ERP Online are substantial, challenges may arise during implementation. This section identifies common challenges faced by organizations adopting ERP Online and provides insights into overcoming these hurdles.
A. Connectivity and Downtime Concerns
Explore how organizations can address concerns related to connectivity and downtime during the transition to ERP Online, ensuring minimal disruptions to daily operations.
B. Customization Complexity
Customization is often necessary to align ERP Online solutions with specific organizational needs. This component delves into the challenges associated with customization complexity and offers guidance on striking the right balance.
C. User Resistance in the Cloud Transition
User resistance can pose a challenge during the transition to cloud-based ERP. Discover strategies to address employee concerns and foster a positive attitude towards ERP Online.
VII. Future Trends in ERP Online
The landscape of ERP Online is continually evolving. This section explores emerging trends and innovations in ERP Online that are expected to shape the future of cloud-based enterprise resource planning.
A. AI and Machine Learning Integration
Examine how the integration of AI and machine learning in ERP Online solutions is enhancing data analysis, predictive capabilities, and automation, contributing to smarter and more efficient organizational management.
B. Edge Computing in ERP
Discover the potential of edge computing in ERP Online, enabling organizations to process data closer to the source, reduce latency, and enhance overall system performance.
C. Enhanced User Experience with UX/UI Innovations
Explore how advancements in user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design are revolutionizing the way users interact with ERP Online solutions, focusing on intuitiveness and accessibility.
VIII. Selecting the Right ERP Online Solution
Choosing the right ERP Online solution is a critical decision for organizations. This section provides guidance on key considerations and factors to weigh when selecting the most suitable ERP Online solution for specific organizational needs.
A. Scalability and Customization Options
Evaluate the scalability and customization options of ERP Online solutions to ensure they align with the evolving needs and growth of the organization over time.
B. Data Security and Compliance Features
Considerations related to data security and compliance are pivotal. This subsection discusses the importance of robust security features and compliance capabilities in ERP Online solutions.
C. Integration with Third-Party Applications
Assess the ease of integration with third-party applications to ensure a seamless flow of data between ERP Online solutions and other essential business tools.
IX. Conclusion
In conclusion, ERP Online stands as a transformative force in the realm of enterprise resource planning, offering organizations a dynamic and scalable solution for managing their operations in the digital age. From its inception to the current landscape of cloud-based ERP solutions, the journey has been marked by innovation, efficiency, and a commitment to meeting the evolving needs of businesses. As organizations continue to embrace the benefits of ERP Online, the future holds exciting possibilities with advancements in technologies like AI, machine learning, and edge computing reshaping the way businesses approach resource planning and management. ERP Online has indeed unleashed the power of the cloud, enabling organizations to thrive in an era of digital transformation.

Acumatica ERP
A. Definition and Overview
Acumatica ERP is a cloud-based, integrated business management solution designed to empower organizations with flexible and scalable tools for managing various aspects of their operations. This section provides an in-depth definition and overview of Acumatica, highlighting its cloud-native architecture and the core functionalities that set it apart in the ERP landscape.
B. Evolution of Acumatica ERP
The evolution of Acumatica ERP is essential to understanding its capabilities and the technological advancements that have shaped its development. This subsection traces the historical journey of Acumatica, from its inception to its current position as a leading player in the ERP market.II. Key Features of Acumatica ERP
Acumatica ERP is distinguished by its feature-rich architecture, addressing the diverse needs of modern businesses. This section breaks down the key features that define Acumatica and explores how they contribute to its effectiveness as a comprehensive business management solution.1. Cloud-Native Architecture
The cloud-native architecture of Acumatica is a fundamental aspect of its design. This subsection delves into the benefits of a cloud-based approach, including scalability, accessibility, and the ability to adapt to evolving business needs.2. Flexible Deployment Options
Acumatica offers flexibility in deployment, allowing organizations to choose between public cloud, private cloud, or on-premises installations. Explore how this flexibility caters to different business requirements and IT preferences.3. Comprehensive Financial Management
Financial management is a cornerstone of Acumatica ERP. This component discusses how Acumatica streamlines accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting, providing organizations with accurate and real-time financial insights.4. Project Accounting and Management
For organizations engaged in projects, Acumatica’s project accounting and management capabilities are crucial. This part explores how Acumatica facilitates project tracking, resource allocation, and collaboration for enhanced project success.III. Industry Applications of Acumatica ERP
The versatility of Acumatica extends across various industries. This section explores how Acumatica is applied in different sectors, including manufacturing, distribution, retail, and services, showcasing its adaptability to diverse business environments.A. Manufacturing Industry
Discover how Acumatica addresses the specific needs of the manufacturing sector, from inventory management to production planning, fostering operational efficiency and responsiveness.B. Distribution and Supply Chain Management
Explore the role of Acumatica in optimizing distribution and supply chain operations, ensuring timely deliveries, minimizing stockouts, and enhancing overall supply chain visibility.C. Retail Management
For the retail industry, Acumatica offers tailored solutions for inventory control, order processing, and customer relationship management. Delve into how retailers leverage Acumatica to enhance customer experiences.D. Service-Based Businesses
In service-based industries, Acumatica aids in project management, resource allocation, and service delivery. This component discusses how service-oriented businesses leverage Acumatica for improved operational efficiency.IV. Implementation Strategies for Acumatica ERP
Implementing Acumatica ERP involves careful planning and execution. This section outlines key strategies for a successful Acumatica implementation, covering considerations such as data migration, user training, and customization.A. Data Migration Best Practices
Effective data migration is critical for a seamless transition to Acumatica ERP. Explore best practices for planning and executing data migration, ensuring accuracy and integrity throughout the process.B. User Training and Change Management
User adoption is pivotal for the success of any ERP implementation. This part emphasizes the importance of comprehensive user training programs and effective change management strategies to facilitate a smooth transition for employees.C. Customization for Business Specificity
Acumatica’s flexibility allows for customization to align with specific business needs. This subsection delves into the customization options offered by Acumatica and how organizations can tailor the system to suit their unique requirements.V. Advantages of Acumatica ERP Adoption
Adopting Acumatica ERP brings forth a multitude of advantages for organizations seeking a modern and scalable business management solution. This section systematically outlines these benefits, showcasing how Acumatica positively impacts various facets of organizational management.A. Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
Explore how Acumatica’s subscription-based model contributes to cost-effectiveness, and its scalable architecture allows organizations to adapt to changing business demands without significant additional costs.B. Real-Time Insights for Informed Decision-Making
Acumatica provides real-time insights, enabling informed decision-making. This subsection discusses how organizations leverage Acumatica to access accurate data, analyze trends, and make strategic decisions promptly.C. Collaboration and Remote Accessibility
In an era of remote work, Acumatica facilitates collaboration and accessibility. Delve into how the platform enables teams to collaborate seamlessly and access critical information from anywhere with an internet connection.VI. Case Studies: Successful Acumatica ERP Implementations
Real-world examples provide tangible evidence of the effectiveness of Acumatica ERP. This section presents case studies of organizations that have successfully implemented Acumatica, showcasing the transformative impact on their operations.A. Global Manufacturer: Streamlining Operations Across Borders
Explore how a global manufacturer streamlined its operations, improved supply chain visibility, and enhanced collaboration across international locations through the successful implementation of Acumatica.B. Growing E-commerce Business: Managing Orders and Inventory Efficiently
Delve into the case study of a burgeoning e-commerce business that leveraged Acumatica to efficiently manage orders, optimize inventory, and accommodate rapid business growth.VII. Challenges in Acumatica ERP Implementation
While the benefits of Acumatica ERP are substantial, challenges may arise during implementation. This section identifies common challenges faced by organizations adopting Acumatica and provides insights into overcoming these hurdles.A. Data Security Concerns in the Cloud Environment
Security in the cloud environment is a paramount concern. Explore how organizations address data security concerns when transitioning to Acumatica, ensuring the protection of sensitive information.B. Integration Complexity with Existing Systems
Integrating Acumatica with existing systems can pose challenges. This subsection discusses strategies for overcoming integration complexities and ensuring seamless data flow between Acumatica and other business applications.C. Change Management in Organizations
Change management within organizations can impact the success of Acumatica implementation. Discover strategies to address employee resistance and foster a positive attitude towards the new ERP system.VIII. Future Trends in Acumatica ERP
The landscape of Acumatica ERP is continually evolving. This section explores emerging trends and innovations in Acumatica ERP that are expected to shape the future of cloud-based enterprise resource planning.A. Advanced Analytics and Business Intelligence
Examine how the integration of advanced analytics and business intelligence in Acumatica ERP is enhancing data-driven decision-making and providing organizations with deeper insights into their operations.B. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
Discover the potential of integrating Internet of Things (IoT) technology with Acumatica ERP, enabling organizations to gather real-time data from connected devices and optimize various processes.C. Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Predictive Analysis
Explore the role of artificial intelligence in Acumatica ERP, particularly in predictive analysis, risk management, and automation, contributing to more proactive and efficient business operations.IX. Selecting the Right Acumatica ERP Partner
Choosing the right Acumatica ERP partner is crucial for organizations embarking on the implementation journey. This section provides guidance on key considerations and factors to weigh when selecting the most suitable Acumatica ERP partner.A. Industry Expertise and Experience
Evaluate the industry expertise and experience of Acumatica ERP partners to ensure they understand the unique needs and challenges of your specific business sector.B. Support and Training Programs
Assess the support and training programs offered by Acumatica ERP partners to ensure a smooth implementation process and ongoing assistance for your organization.C. Customization Capabilities and Flexibility
Consider the customization capabilities and flexibility offered by Acumatica ERP partners to tailor the system to align with the unique requirements of your organization.X. Conclusion
In conclusion, Acumatica ERP stands as a powerful and adaptable solution that empowers organizations to navigate the complexities of modern business environments. From its inception to its current standing, Acumatica has demonstrated a commitment to innovation, flexibility, and delivering tangible value to businesses across various industries. As organizations continue to seek scalable and cloud-native ERP solutions, Acumatica’s role in shaping the future of enterprise resource planning remains significant.
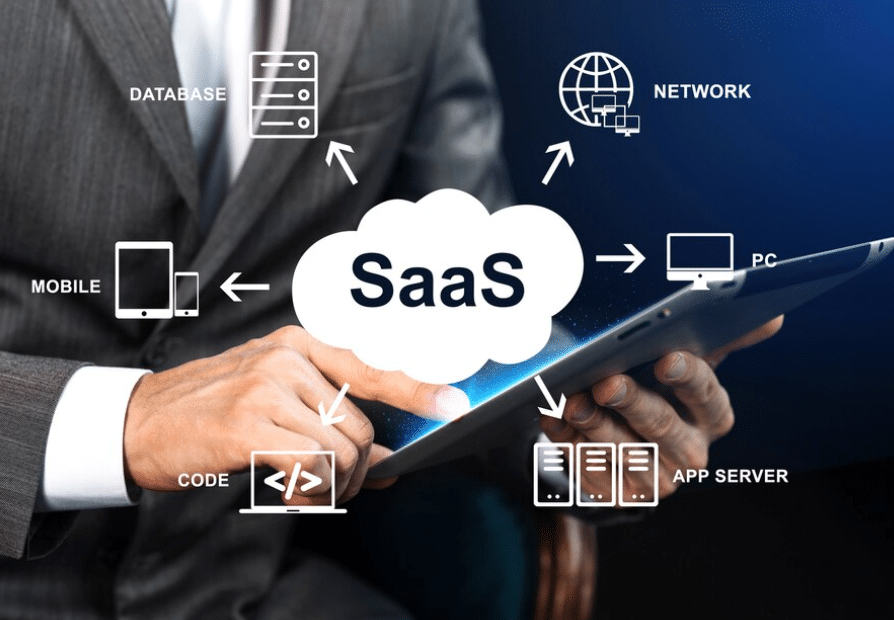
SaaS ERP
stands for “Software as a Service Enterprise Resource Planning.” But let’s break that down into simpler terms. Imagine your business as a grand puzzle. Each piece represents a different aspect of your operations – from finances to inventory management, human resources to customer relations. SaaS ERP is the magical glue that seamlessly connects these pieces together. It’s like having a master conductor directing the orchestra, ensuring every note is in harmony.

In essence, SaaS ERP is a cloud-based software that streamlines and integrates various core functions of your business. This includes accounting, procurement, project management, HR, and more. All this is achieved without the hassle of traditional software installations, as everything is hosted on the cloud. Traditional ERP systems come with substantial upfront costs. Buying licenses, investing in hardware, and setting up the infrastructure can put a dent in your budget before you even begin. On the other hand, SaaS ERP operates on a subscription basis. It’s like paying a monthly rent for an apartment rather than buying the entire building. This means you can get started without a significant initial investment. It’s budget-friendly and reduces financial strain, especially for small and medium-sized businesses.
Understanding the SaaS Advantage
Now, you might wonder, “Why should I choose SaaS ERP over traditional software?” Well, that’s a great question. SaaS ERP offers a multitude of benefits. One of the key advantages of SaaS ERP is its scalability. Think of it as a piece of elastic that can stretch or shrink as needed. Traditional systems often struggle to accommodate growth, but with SaaS ERP, you can scale up or down effortlessly. As your business expands or contracts, your ERP system adapts accordingly. This scalability ensures that your ERP system remains a perfect fit for your business, whether you’re a start-up or a well-established enterprise.
- Cost-Effective: Traditional ERP systems come with substantial upfront costs. SaaS ERP, on the other hand, operates on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for hefty investments in software and hardware.
- Scalability: SaaS ERP is flexible and can adapt to your business’s evolving needs. You can scale up or down as required without major disruptions.
- Accessibility: The cloud-based nature of SaaS ERP ensures you can access your data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This is especially handy for businesses with remote teams or multiple locations.
- Automatic Updates: Say goodbye to the hassle of manual software updates. SaaS ERP providers handle this for you, ensuring your system is always up-to-date and secure.
- Streamlined Collaboration: With SaaS ERP, collaboration between departments becomes a breeze. Data is shared in real-time, fostering better decision-making and teamwork.
How SaaS ERP Works
To demystify this further, think of SaaS ERP as your personal wizard. It centralizes your data, making it available to all relevant departments. Let’s say your sales team lands a big contract. With SaaS ERP, the sales department can instantly update inventory levels, prompting the procurement department to restock. Simultaneously, the finance team can prepare for incoming revenue, all while HR plans to onboard new staff to meet the demand. In simpler terms, SaaS ERP automates workflows, reducing manual tasks, errors, and delays. It’s your business’s best friend, ensuring that everything runs smoothly. The cloud-based nature of SaaS ERP ensures that your business is always within reach. It’s like having your office in your pocket. Whether you’re at your desk, in a coffee shop, or even traveling, as long as you have an internet connection, you can access your SaaS ERP. This is a game-changer for businesses with remote teams, multiple locations, or employees on the go. Your data and applications are at your fingertips, ensuring you can make informed decisions and take action wherever you are.
Choosing the Right SaaS ERP Solution
Selecting the perfect SaaS ERP solution for your business can be a daunting task, like picking the right car from a showroom with countless options. Here are some key points to consider, Traditional software often requires manual updates. It’s like maintaining a car – you need to regularly check, repair, and upgrade various parts. SaaS ERP simplifies this by handling updates automatically. It’s akin to a self-updating car that not only performs maintenance itself but also continuously improves its performance. With SaaS ERP, you can be confident that your system is always up-to-date, secure, and equipped with the latest features. Say goodbye to the hassle of managing updates and patches, leaving you with peace of mind to focus on your core business.
- Business Needs: Identify your specific requirements. Do you need robust financial management, comprehensive reporting, or a focus on supply chain management? Choose a solution that aligns with your goals.
- Scalability: Ensure the software can grow with your business. You don’t want to outgrow your ERP solution and face the hassle of migration.
- User-Friendly Interface: The best SaaS ERP solutions offer intuitive interfaces that your team can quickly adapt to.
- Vendor Reputation: Research the vendor’s reputation. Read reviews, ask for references, and ensure they have a track record of delivering quality service and support.
- Data Security: Your data is invaluable. Choose a SaaS ERP solution with robust security measures in place to protect your information.
SaaS ERP in Action: Real-Life Examples
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s see how SaaS ERP is making a real impact. Two prime examples are, Imagine your business as a complex network of departments, each with its specific tasks and responsibilities. SaaS ERP acts as the bridge that connects these departments seamlessly. It’s like a superhighway for data, ensuring it flows freely across your organization. With real-time data sharing and collaboration tools, SaaS ERP fosters better decision-making and teamwork. It breaks down the silos between departments, making information accessible to those who need it, when they need it. This seamless collaboration results in improved efficiency, enhanced productivity, and ultimately, better outcomes for your business. In conclusion, the SaaS advantage is all about cost-effectiveness, scalability, accessibility, automatic updates, and streamlined collaboration. These benefits make SaaS ERP a powerful choice for businesses of all sizes, helping them streamline operations, boost productivity, and stay competitive in an ever-evolving marketplace. So, if you want to take your business to the next level, it’s time to embrace the advantages of SaaS ERP.
- Salesforce: Known for its customer relationship management (CRM) capabilities, Salesforce uses SaaS ERP to streamline sales processes, manage customer data, and provide actionable insights.
- NetSuite: This cloud-based ERP system is favored by a wide range of industries, offering comprehensive solutions for finance, HR, and e-commerce.
Measuring the ROI of SaaS ERP
Return on Investment (ROI) is a crucial metric for any business decision. SaaS ERP offers a significant return through increased productivity, cost savings, and improved decision-making. As your business operations become more efficient, the ROI of your SaaS ERP investment becomes increasingly evident. It’s like planting seeds that grow into flourishing trees. Create a detailed migration plan that outlines what data needs to be moved, in what order, and how. Before the migration, ensure that you have a reliable backup of all your data. This serves as a safety net in case of any unexpected issues during the migration.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Every journey has its challenges, and implementing SaaS ERP is no exception. Here are some hurdles you might encounter, Every journey has its challenges, and implementing SaaS ERP is no exception. It’s like embarking on an adventure filled with obstacles and hurdles. However, with the right strategies and preparation, you can overcome these challenges and ensure a successful transition to SaaS ERP.
- Data Migration: Moving your data from legacy systems can be complex. Ensure a smooth transition plan and backup measures.
- User Adoption: Introducing a new system can be met with resistance. Provide proper training and incentives to encourage adoption.
- Integration: Ensuring SaaS ERP integrates seamlessly with your existing software is vital for uninterrupted operations.
- Customization: Tailoring the software to your unique needs might require technical expertise. Be prepared to invest in customization if necessary.
Security in the SaaS ERP World
Security is a top concern, much like guarding a treasure chest. SaaS ERP providers invest heavily in security measures to protect your data. They employ encryption, secure data centers, and regular security audits to ensure your information remains confidential and safe. Consider involving professionals who specialize in data migration to ensure a smooth and secure transfer. Introducing a new system to your team can be met with resistance. Change can be intimidating, and some employees may be hesitant to embrace the new technology. To overcome this challenge.
The Future of SaaS ERP
SaaS ERP is continually evolving. We can liken it to a dynamic river, always flowing and adapting. With advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, SaaS ERP is becoming smarter, offering predictive analytics and even more seamless integration. As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, SaaS ERP will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of operations. Ensuring that SaaS ERP integrates seamlessly with your existing software is vital for uninterrupted operations. It’s like ensuring all the pieces of a puzzle fit perfectly together. To overcome this challenge:
- Choose Compatible Software: When selecting a SaaS ERP solution, make sure it is compatible with the other software your business relies on.

Great Plains Accounting Software
Great Plains Accounting Software-In the realm of accounting software solutions, Great Plains Accounting Software stands out as a robust and versatile tool designed to streamline financial processes, enhance reporting capabilities, and empower businesses with comprehensive financial management. This article embarks on a comprehensive exploration of Great Plains Accounting Software, providing an in-depth understanding of its definition, historical evolution, key features, benefits, industry applications, implementation strategies, and future trends.
Introduction
A. Definition and Overview
Great Plains Accounting Software, now known as Microsoft Dynamics GP, is an integrated business management solution that encompasses accounting, financial management, and operational functionalities. This section introduces the software, highlighting its core features and its role in facilitating efficient financial operations for organizations.B. Evolution of Great Plains Accounting Software
The evolution of Great Plains Accounting Software is crucial to understanding its current capabilities and the technological advancements that have shaped its development. This subsection traces the historical journey of the software, from its origins to its integration into the Microsoft Dynamics suite.II. Key Features of Great Plains Accounting Software
Great Plains Accounting Software is renowned for its feature-rich platform. This section delves into the key features that define the software and explores how these functionalities contribute to its effectiveness as an accounting solution.1. General Ledger Management
At the core of Great Plains Accounting Software is its General Ledger management. This subsection explores how the software facilitates the tracking and management of financial transactions, ensuring accuracy and compliance with accounting standards.2. Accounts Payable and Receivable
Efficient management of accounts payable and receivable is essential for financial stability. This component discusses how Great Plains Accounting Software streamlines invoicing, payment processing, and receivables management.3. Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting and forecasting are critical for strategic financial planning. Explore how Great Plains Accounting Software enables organizations to create, manage, and analyze budgets, aiding in better decision-making.4. Financial Reporting and Analysis
Comprehensive financial reporting and analysis are key strengths of Great Plains Accounting Software. This part delves into the reporting tools and analytical capabilities that empower organizations to extract valuable insights from financial data.III. Benefits of Great Plains Accounting Software
The adoption of Great Plains Accounting Software offers a myriad of benefits for organizations seeking to elevate their financial management processes. This section systematically outlines these advantages, showcasing how the software positively impacts various facets of accounting and financial operations.A. Improved Efficiency and Accuracy
Great Plains Accounting Software enhances efficiency by automating repetitive tasks and reducing manual data entry. Explore how this results in increased accuracy and time savings for accounting professionals.B. Enhanced Financial Visibility
Financial visibility is paramount for effective decision-making. This subsection discusses how Great Plains Accounting Software provides real-time insights into financial data, fostering a clear understanding of an organization’s financial health.C. Streamlined Compliance and Reporting
Navigating regulatory compliance is simplified with Great Plains Accounting Software. Delve into how the software assists organizations in meeting reporting requirements and staying compliant with accounting standards.IV. Industry Applications of Great Plains Accounting Software
Great Plains Accounting Software is versatile and finds applications across various industries. This section explores how the software caters to the unique accounting and financial management needs of sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, services, and more.A. Manufacturing Industry
Discover how Great Plains Accounting Software addresses the specific accounting challenges faced by manufacturing companies, from inventory tracking to cost management.B. Healthcare Sector
In the healthcare sector, financial management is complex. This component discusses how Great Plains Accounting Software aids healthcare organizations in managing finances, billing, and compliance.C. Professional Services
For professional services firms, accurate billing and financial management are critical. Explore how Great Plains Accounting Software supports service-oriented businesses in maintaining financial efficiency.V. Implementation Strategies for Great Plains Accounting Software
Implementing Great Plains Accounting Software requires careful planning and execution. This section outlines key strategies for a successful implementation, covering considerations such as data migration, user training, and customization.A. Data Migration Best Practices
Effective data migration is crucial for a smooth transition to Great Plains Accounting Software. Explore best practices for planning and executing data migration, ensuring accuracy and integrity throughout the process.B. User Training and Change Management
User adoption is pivotal for the success of any accounting software implementation. This part emphasizes the importance of comprehensive user training programs and effective change management strategies.C. Customization for Business Specificity
Great Plains Accounting Software offers customization options to align with specific business needs. This subsection delves into how organizations can tailor the software to suit their unique accounting and financial requirements.VI. Challenges in Great Plains Accounting Software Implementation
While the benefits of Great Plains Accounting Software are substantial, challenges may arise during implementation. This section identifies common challenges faced by organizations adopting the software and provides insights into overcoming these hurdles.A. Integration Complexity with Existing Systems
Integrating Great Plains Accounting Software with existing systems can pose challenges. This subsection discusses strategies for overcoming integration complexities and ensuring seamless data flow between systems.B. User Resistance and Training Issues
User resistance is a common challenge in software implementations. Explore strategies to address employee resistance and foster a positive attitude towards using Great Plains Accounting Software.C. Customization Complexity
While customization is a strength, it can also present challenges. This component delves into the complexities associated with customization and offers guidance on finding the right balance.VII. Case Studies: Successful Great Plains Accounting Software Implementations
Real-world examples provide tangible evidence of the effectiveness of Great Plains Accounting Software. This section presents case studies of organizations that have successfully implemented the software, showcasing the transformative impact on their financial management.A. Mid-sized Manufacturing Company: Streamlining Financial Operations
Explore how a mid-sized manufacturing company streamlined its financial operations, improved reporting accuracy, and enhanced compliance through the successful implementation of Great Plains Accounting Software.B. Healthcare Facility: Financial Management Efficiency
Delve into the case study of a healthcare facility that leveraged Great Plains Accounting Software to enhance financial management efficiency, streamline billing processes, and improve overall financial visibility.VIII. Future Trends in Great Plains Accounting Software
The landscape of accounting software is continually evolving, and Great Plains Accounting Software is no exception. This section explores emerging trends and innovations that are expected to shape the future of Great Plains Accounting Software.A. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
Examine how the integration of artificial intelligence in Great Plains Accounting Software is enhancing automation, data analysis, and providing intelligent insights for more informed financial decision-making.B. Mobile Accessibility and Remote Capabilities
Discover the growing importance of mobile accessibility and remote capabilities in accounting software. Explore how Great Plains Accounting Software is adapting to the trend of remote work and on-the-go financial management.C. Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures
In an era of increasing cyber threats, cybersecurity measures are paramount. This component discusses how Great Plains Accounting Software is evolving to incorporate enhanced security features to protect financial data.IX. Selecting the Right Great Plains Accounting Software Partner
Choosing the right Great Plains Accounting Software partner is crucial for organizations embarking on the implementation journey. This section provides guidance on key considerations and factors to weigh when selecting the most suitable partner.A. Experience and Expertise
Evaluate the experience and expertise of potential Great Plains Accounting Software partners to ensure they understand the unique accounting needs of your organization.B. Support and Training Offerings
Assess the support and training programs offered by Great Plains Accounting Software partners to ensure a smooth implementation process and ongoing assistance for your organization.C. Customization Capabilities and Flexibility
Consider the customization capabilities and flexibility offered by Great Plains Accounting Software partners to tailor the system to align with the unique requirements of your organization.X. Conclusion
In conclusion, Great Plains Accounting Software remains a stalwart in the realm of financial management solutions, offering organizations a comprehensive platform to navigate the complexities of accounting and enhance overall financial efficiency. From its historical evolution to its current standing within the Microsoft Dynamics suite, Great Plains Accounting Software has consistently evolved to meet the changing needs of businesses across various industries. As organizations continue to seek powerful and adaptable accounting solutions, the future holds exciting possibilities with trends such as AI integration, mobile accessibility, and enhanced cybersecurity reshaping the landscape.