The Evolution of SIM Cards in IoT Devices has been a fascinating journey, from their initial use in bulky cellular phones to their vital role in connecting the ever-growing network of smart devices. This evolution reflects the relentless drive for miniaturization, increased functionality, and seamless connectivity in the Internet of Things (IoT) landscape.
The early days of IoT saw SIM cards, those small chips that store your phone number and network information, playing a crucial role in connecting devices to cellular networks. However, these early SIM cards were bulky, expensive, and consumed a lot of power, limiting their application in resource-constrained IoT devices.
As the demand for smaller, more power-efficient, and multi-functional devices grew, the evolution of SIM card technology took center stage.
The Rise of SIM Cards in IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) revolutionized how we interact with the world, and SIM cards played a crucial role in connecting these devices to cellular networks. As the IoT landscape expanded, SIM cards became integral components, enabling seamless communication and data transfer between devices and the internet.
Early Adoption of SIM Cards in IoT
The initial adoption of SIM cards in IoT devices was driven by the need for reliable connectivity in remote locations and the desire to leverage existing cellular infrastructure. Early adopters recognized the potential of SIM cards to connect a wide range of devices, from industrial sensors to smart meters, to the internet.
- Industrial Monitoring:Early IoT applications using SIM cards focused on industrial monitoring and control. Industrial sensors, equipped with SIM cards, transmitted real-time data about temperature, pressure, and other critical parameters to central monitoring systems, enabling remote monitoring and proactive maintenance.
- Smart Metering:SIM cards were also integrated into smart meters, allowing utilities to remotely monitor energy consumption and bill customers accurately. These smart meters used SIM cards to transmit usage data to utility companies, improving efficiency and reducing energy waste.
- Telematics:In the automotive industry, SIM cards enabled vehicle tracking and fleet management. Telematics devices, equipped with SIM cards, provided real-time location data, fuel consumption information, and diagnostic data, allowing fleet managers to optimize routes, improve efficiency, and ensure safety.
Early Challenges with SIM Cards in IoT
Despite the early success of SIM cards in IoT, several challenges hindered their widespread adoption. These challenges primarily revolved around size, cost, and power consumption.
- Size and Form Factor:Traditional SIM cards were too large and bulky for many IoT devices, especially those with limited space. The miniaturization of SIM cards, such as micro-SIMs and nano-SIMs, was crucial for accommodating the space constraints of smaller IoT devices.
- Cost:The cost of SIM cards and associated data plans was a significant barrier for some IoT applications. The high cost of SIM cards, particularly for large deployments, limited the adoption of IoT solutions in cost-sensitive sectors.
- Power Consumption:SIM cards, especially in early iterations, consumed significant power, impacting the battery life of battery-powered IoT devices. Efforts to reduce power consumption were essential for making SIM cards suitable for long-lasting IoT deployments.
Evolution of SIM Card Technologies
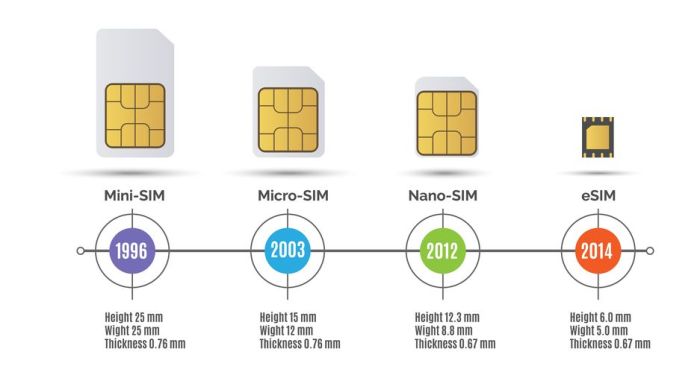
The SIM card, a small chip that stores subscriber information and enables mobile communication, has undergone a remarkable evolution, particularly in the context of IoT devices. As IoT devices became smaller and more ubiquitous, the need for miniaturized SIM cards became increasingly apparent.
This evolution has not only impacted device size but also introduced new capabilities and benefits for IoT applications.
Transition to Smaller Form Factors
The transition from traditional SIM cards to smaller form factors like micro-SIM and nano-SIM has been driven by the relentless pursuit of device miniaturization.
- Traditional SIM:The original SIM card, measuring 25mm x 15mm, was introduced in the early 1990s. It was relatively large and bulky, limiting its use in smaller devices.
- Micro-SIM:Introduced in 2003, the micro-SIM card reduced the size to 15mm x 12mm, enabling the development of more compact mobile phones.
- Nano-SIM:The nano-SIM, introduced in 2012, further reduced the size to 12.3mm x 8.8mm. This miniaturization was crucial for the development of even smaller smartphones and other mobile devices.
These smaller form factors have enabled the development of increasingly compact IoT devices, such as wearables, smart home sensors, and industrial equipment. The miniaturization of SIM cards has played a crucial role in the proliferation of IoT devices, allowing for their integration into diverse and often space-constrained environments.
Embedded SIM (eSIM) Technology
The emergence of embedded SIM (eSIM) technology has revolutionized SIM card functionality, particularly in the context of IoT.
- eSIM:An eSIM is a programmable chip embedded directly into a device, eliminating the need for a removable SIM card. This technology allows for remote provisioning, multi-carrier support, and simplified device management.
The ability to provision an eSIM remotely eliminates the need for physical SIM card swaps, simplifying device deployment and management. Moreover, eSIMs can support multiple mobile operators, providing flexibility and reducing the need for device-specific SIM cards.
Comparison of SIM Card Technologies for IoT
The choice of SIM card technology for IoT applications depends on various factors, including device size, connectivity requirements, and management needs.
| SIM Card Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional SIM | Widely available, cost-effective | Large size, requires physical swap | Legacy devices, low-cost applications |
| Micro-SIM | Smaller than traditional SIM, widely available | Requires physical swap | Compact devices, where size is a constraint |
| Nano-SIM | Smallest form factor, suitable for miniaturized devices | Requires physical swap | Smartphones, wearables, compact IoT devices |
| eSIM | Remote provisioning, multi-carrier support, simplified management | Higher initial cost, requires device support | Smartphones, wearables, industrial IoT devices, smart home devices |
As IoT devices become increasingly sophisticated and interconnected, eSIM technology is poised to play a pivotal role in enabling seamless connectivity and efficient management.
SIM Cards in Diverse IoT Applications
SIM cards are not just for smartphones anymore. They have become integral components in a wide range of IoT devices, enabling connectivity and communication in various applications. From smart homes to industrial automation, SIM cards play a crucial role in connecting devices, collecting data, and facilitating seamless operation.
Smart Homes
SIM cards enable smart home devices to connect to the internet, allowing users to remotely control and monitor their homes.
- Smart Security Systems:Security cameras, motion sensors, and door locks use SIM cards to send alerts and notifications to homeowners in case of intrusion or other security breaches.
- Smart Appliances:Refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens with embedded SIM cards can be remotely controlled and monitored, allowing users to adjust settings, receive notifications, and even order groceries online.
- Smart Lighting:Smart bulbs and lighting systems utilize SIM cards to connect to the internet, enabling users to control lighting levels, set schedules, and create custom lighting scenarios.
SIM cards in smart homes offer convenience, security, and energy efficiency. They allow users to remotely control and monitor their homes, receive real-time alerts, and optimize energy consumption.
Wearables
SIM cards in wearables provide connectivity for fitness trackers, smartwatches, and other devices that collect and transmit personal health data.
- Fitness Trackers:Fitness trackers use SIM cards to upload data to fitness apps, allowing users to monitor their activity levels, track progress, and share their achievements.
- Smartwatches:Smartwatches with SIM cards allow users to make calls, send messages, and access internet services without carrying their smartphones. They also enable features like emergency SOS and location tracking.
- Medical Devices:Medical devices like insulin pumps and heart rate monitors use SIM cards to transmit vital data to healthcare professionals, enabling remote monitoring and timely intervention.
SIM cards in wearables enhance user experience by providing seamless connectivity, enabling real-time data sharing, and facilitating personalized health management.
Industrial Automation
SIM cards are essential for industrial automation, enabling communication and data exchange between machines, sensors, and control systems.
- Remote Monitoring and Control:SIM cards allow manufacturers to monitor equipment performance, track production data, and remotely control machines from anywhere in the world.
- Predictive Maintenance:Sensors equipped with SIM cards can collect data on machine health, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Automated Logistics:SIM cards enable real-time tracking of goods in transit, optimizing logistics and improving supply chain efficiency.
SIM cards in industrial automation enhance efficiency, productivity, and safety by providing real-time data insights, enabling remote monitoring and control, and facilitating predictive maintenance.
Smart Cities, The Evolution of SIM Cards in IoT Devices
SIM cards play a crucial role in building smart cities by connecting various infrastructure components and enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Traffic Management:Smart traffic lights and parking sensors use SIM cards to collect traffic data, optimize traffic flow, and reduce congestion.
- Environmental Monitoring:Sensors equipped with SIM cards can monitor air quality, water levels, and other environmental factors, providing real-time data for environmental management and disaster preparedness.
- Smart Street Lighting:Street lights with embedded SIM cards can adjust their brightness based on real-time conditions, reducing energy consumption and improving public safety.
SIM cards in smart cities enable efficient resource management, improved public safety, and enhanced quality of life by facilitating data collection, communication, and real-time decision-making.
Remember to click Best Remote Monitoring & Management (RMM) Software to understand more comprehensive aspects of the Best Remote Monitoring & Management (RMM) Software topic.
Future Trends in SIM Cards for IoT

The SIM card landscape in the IoT is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in connectivity, security, and device capabilities. This evolution is paving the way for a future where SIM cards play an even more critical role in enabling sophisticated and innovative IoT applications.
5G Connectivity and its Impact on SIM Cards
G, the latest generation of wireless technology, is poised to revolutionize IoT by offering significantly faster speeds, lower latency, and greater bandwidth. This will enable the development of new and advanced IoT applications that demand real-time data transfer and high-performance connectivity.
The rise of 5G will necessitate the development of SIM cards that can leverage its capabilities effectively.
5G SIM cards will need to support the higher data rates and advanced features of 5G networks, enabling seamless connectivity for IoT devices.
G SIM cards are expected to play a crucial role in:
* Enabling real-time data analytics and decision-making in industrial IoT applications.For example, in manufacturing, 5G SIM cards will facilitate the rapid transfer of data from sensors and machines, enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of production processes.
- Supporting the deployment of connected vehicles and smart cities.5G SIM cards will be essential for enabling the high-speed data transfer required for autonomous vehicles, traffic management systems, and smart city infrastructure.
- Facilitating the development of immersive and interactive AR/VR applications.5G SIM cards will provide the bandwidth and low latency necessary for seamless AR/VR experiences in various sectors, such as healthcare, education, and entertainment.
eSIM Evolution and its Implications for IoT
eSIMs, or embedded SIMs, are a revolutionary technology that eliminates the need for physical SIM cards. They are embedded directly onto the device’s motherboard, allowing for multiple profiles and seamless switching between carriers. This technology is gaining traction in the IoT space due to its numerous benefits.
eSIMs are particularly advantageous for IoT devices where space is limited and flexibility in connectivity is paramount.
eSIMs will significantly impact the IoT landscape by:* Simplifying device deployment and management.eSIMs eliminate the need for physical SIM card insertion, making device deployment faster and easier. They also facilitate remote SIM provisioning, allowing for simplified management of large-scale IoT deployments.
- Enabling multi-carrier support and roaming.eSIMs allow devices to connect to multiple carriers, offering flexibility and cost optimization. They also enable seamless roaming, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity across different regions.
- Facilitating secure and remote SIM provisioning.eSIMs enable secure and remote provisioning of SIM profiles, eliminating the need for physical access to the device. This is particularly important for IoT devices deployed in remote locations or inaccessible environments.
Secure SIM Solutions for Enhanced Data Protection
Security is paramount in the IoT, especially with the increasing use of connected devices for sensitive applications. Secure SIM solutions are playing a crucial role in protecting data and ensuring the integrity of IoT deployments.
Secure SIM solutions are designed to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access to IoT devices.
These solutions incorporate various security features, such as:* Hardware-based security modules:These modules provide a secure environment for storing sensitive data, such as cryptographic keys and device credentials.
Secure boot and firmware updates
Secure SIM solutions ensure that only trusted software is loaded onto the device and that firmware updates are authenticated.
Secure communication protocols
Secure SIMs support secure communication protocols, such as TLS/SSL, to protect data transmitted over the network.
Future Trends in SIM Cards for IoT: Key Features and Benefits
| Feature | Benefit | Potential Applications ||——————————————|———————————————————————————————————-|—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————|| 5G Connectivity | Faster speeds, lower latency, and greater bandwidth | Industrial IoT, connected vehicles, smart cities, AR/VR applications || eSIMs | Simplified device deployment, multi-carrier support, remote SIM provisioning, and enhanced security | Wearables, smart home devices, industrial sensors, and mobile payment terminals || Secure SIM Solutions | Enhanced data protection, secure boot, and secure communication protocols | Healthcare devices, financial transactions, critical infrastructure, and industrial automation || Integrated Security Modules | Hardware-based security for sensitive data and device credentials | IoT devices handling sensitive data, such as medical records, financial transactions, and personal information || Advanced SIM Management Platforms | Centralized management of SIM profiles, real-time monitoring, and remote SIM provisioning | Large-scale IoT deployments, such as smart cities, industrial automation, and connected vehicles || Over-the-Air (OTA) SIM Profile Updates | Dynamically update SIM profiles and configurations without physical access to the device | Remotely update device settings, security configurations, and carrier profiles, enabling flexibility and scalability in IoT deployments || Support for Multiple Communication Standards | Flexibility in connecting to different cellular networks, including 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G | IoT devices requiring connectivity in diverse environments and regions, supporting a wide range of applications, from basic sensor networks to advanced industrial automation systems || Energy-Efficient SIM Designs | Extended battery life and reduced power consumption for IoT devices | Long-life battery-powered IoT devices, such as environmental sensors, asset trackers, and smart meters, enabling extended deployment in remote locations and reducing operational costs |
Outcome Summary: The Evolution Of SIM Cards In IoT Devices

The future of SIM cards in IoT is bright, with emerging technologies like 5G connectivity, eSIM evolution, and secure SIM solutions paving the way for even more sophisticated and connected devices. As the IoT ecosystem continues to expand, SIM cards will play an increasingly vital role in enabling a world where everything is connected and intelligent.
From smart homes and wearables to industrial automation and smart cities, SIM cards will be the invisible threads connecting these diverse applications, driving innovation and shaping the future of our interconnected world.
FAQ Corner
What are the main challenges faced by SIM cards in IoT?
Some key challenges include limited battery life in devices, security vulnerabilities, and the need for cost-effective solutions for large-scale deployments.
How do eSIMs improve the user experience in IoT?
eSIMs offer remote provisioning, allowing devices to connect to different networks without the need for physical SIM card swaps. This is particularly beneficial for devices with limited user interaction, like smart meters or industrial sensors.
What are the future implications of 5G connectivity for SIM cards in IoT?
5G’s high bandwidth and low latency will enable a wide range of new IoT applications, requiring SIM cards with enhanced capabilities to handle the increased data throughput and real-time communication demands.
What are the security considerations for SIM cards in IoT?
Security is paramount in IoT, and SIM cards play a crucial role in protecting data and ensuring secure communication. Secure SIM solutions with advanced encryption and authentication features are essential to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.